Context
The rearing of healthy European livestock is highly dependent on the provision of high quality and safe feeds. This in turn has a major impact on the safety of the entire animal based food chain. The concept of QSAFFE is to deliver better, faster and economically viable means of ensuring the quality and safety of animal feeds in Europe. The QSAFFE consortium is composed of academics and government scientists with substantial experience in animal feed research along with industrial companies, large and small, dedicated to supplying and producing higher quality and safer animal feeds. Together, their vision is an integrated approach to the reduction and management of chemical and microbiological contamination in animal feeds. This research project will provide better ways of preventing contamination and fraud, identifying and assessing new risks and providing scientific evidence of the risks of transfer of microbiological and chemical contaminants from feed to food.
Objectives
There are four core scientific and technological objectives within QSAFFE linked to a comprehensive training and dissemination plan: - Strategies for the early Quality and Safety Assurance in the Feed Chain: QSAFFE will undertake an intensive investigation regarding combining existing testing methods and emerging technologies, including fingerprinting technologies, into a comprehensive analytical strategy to determine the best application for feed material quality and safety monitoring at ports, feed mills and laboratories. - -Feed Materials Traceability and Authenticity: QSAFFE will develop and improve systems of traceability and authenticity monitoring of the major feed materials used in Europe. This will be achieved by determining which analytical techniques (conventional and fingerprinting) could be useful tools in tracing origins of feed materials including those derived from biofuel co-products. - Emerging Risks: QSAFFE will identify the emerging risks (chemical and microbiological) from new sources of animal feed materials that may arise from changes to the formulation/composition of animal feeds and due to economic factors. New sources of animal feed materials are being sought due to the increasing costs of many of the current materials. The new sources can apply to novel materials and/or new geographical sources of the existing materials. The risks and benefits of such practices are not clearly defined and research is required to devise strategies to ensure quality and safety of such new animal feed components and sources of materials. - Transfer of contaminants and micro-organisms from feed to food: QSAFFE will undertake optimization and application of pharmaco-kinetic models focussing on a number of carefully selected transfer problems such as dioxins and PCBs, melamine and related compounds, Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes based on existing data and data generated in the studies performed within the project. QSAFFE will perform transfer studies on a number of highly important feed contaminants i.e. transfer of melamine and related compounds from feed to eggs and transfer of dioxins and PCBs to sheep livers and meat due to the presence of contaminated soil in fodder. The Ultimate Goal is to provide Europe with a framework for improving the quality and safety of animal feeds entering at ports from outside the EU as well as products produced within Europe. To achieve these objectives, six workpackages have been defined. -WP1: Strategies for the Early Quality and Safety Assurance in the feed chain -WP2: Feed Materials Traceability and Authenticity -WP3: Emerging Risks -WP4: Transfer of contaminants and micro-organisms from feed to food -WP5: Dissemination activities -WP6: Management activities
Expected results
The outcomes of QSAFFE must be valued by Europe and extendable worldwide. To ensure this, we have a full and targeted dissemination plan. QSAFFE will consolidate and deliver its findings by building and maintaining a project website (http://www.qsaffe.eu), establishing a stakeholder database, publishing an e-Newsletter, training and knowledge transfer, peer reviewed publications, training workshops, organising an international conference and the publication of guidance documents on improving traceability and authenticity for the feed industry.
Results obtained
All these results presented here can be found in the QSAFFE website (http://www.qsaffe.eu ), especially in the 3rd Newsletter- July 2014 and in the different Deliverables and papers published during the running of the project.
Regarding the CRA-W contribution, three main studies and outputs have been delivered:
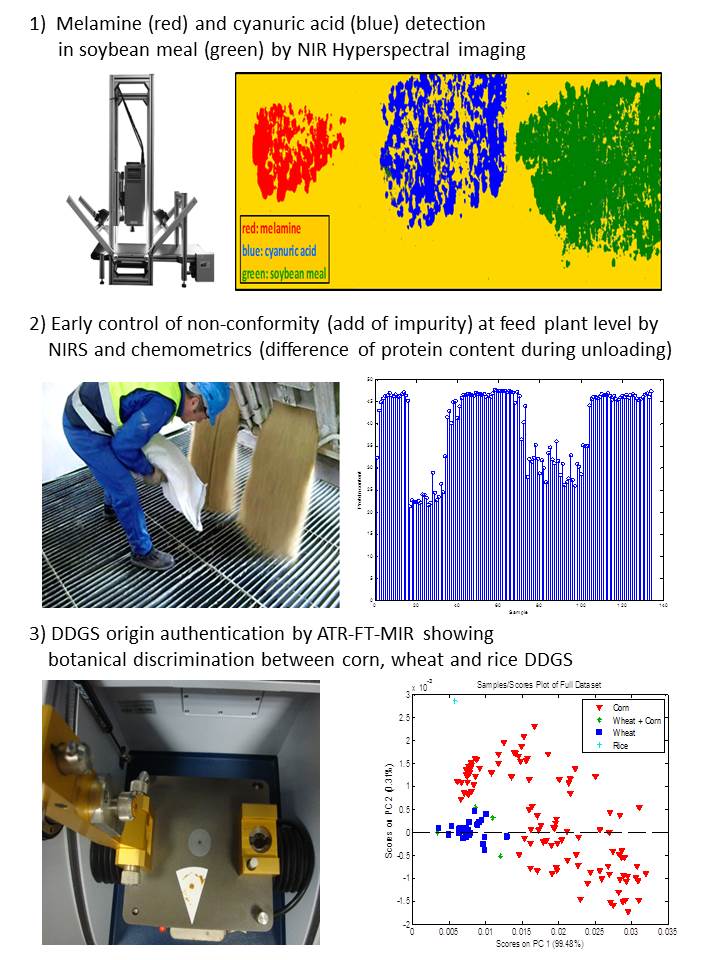
1) The first study was aimed at exploring the feasibility of detecting and quantifying melamine, and its structural analogue cyanuric acid, in soybean meal, using line-scan near infrared hyperspectral imaging spectroscopy (NIR-HIS). The aim is to avoid repetition of recent cases of deliberate melamine contamination of soybean meal and to prevent future contaminations. For this study, a total of 40 commercial soybean meal samples were collected, and 17 adulterated samples were prepared by adding different amounts of melamine/cyanuric acid to the samples, with concentrations varying between 0.5% and 5%. The spectral data were collected using line-scan NIR–HIS, and partial least-squares discriminant analysis was used to obtain a discrimination model and a semi-quantitative prediction of the content of contaminants. This study has permitted the detection of low levels of melamine and also revealed some limitations for the feasibility of quantifying melamine in soybean meal.
Two papers based on these results have been published:
Fernández Pierna, J.A., Vincke, D., Dardenne, P., Zengling, Yang, Lujia, Han & Baeten, V. (2014). Line scan hyperspectral imaging spectroscopy for the early detection of melamine and cyanuric acid in feed. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 22: (2), 103-112.
Baeten, V., Vermeulen, P., Fernández Pierna, J.A. & Dardenne, P. (2014). From targeted to untargeted detection of contaminants and foreign bodies in food and feed using NIR spectroscopy NewFood 17, (3), 15-23.
2) The objective of the second study was to devise a complete procedure based on chemometrics and NIR spectroscopy at the entrance of a feed mill to provide early evidence of non-conformity and unusual ingredients and thus help to achieve cost-savings. The procedure was validated at laboratory level and adapted for application at the Cargill Animal Nutrition feed mill. The study focused on the characterisation of soybean meal. The results showed that the use of NIR, combined with some chemometric tools based on distances and residuals from regression equations, is appropriate for authenticating feed products and detecting the presence of abnormal samples or impurities in both the laboratory and at the feed mill.
A paper based on these results has been published:
Fernández Pierna, J.A. , Abbas, O. , Lecler, B. , Hogrel, P. , Dardenne, P. & Baeten, V. (2014). NIR fingerprint screening for early control of non-conformity at feed mills. Food Chemistry, accepted.
3) The third study applied attenuated total reflection Fourier transform mid-infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FT-MIR) to identify the origin of DDGS. The authentication was based on analyzing only the composition of the DDGS oil fraction, The originality of the method lies in the in situ extraction of the oil, without solvent or chemical transformation, thus preventing possible influences on the composition of the oil and reducing drastically the analytical time. The use of spectroscopic and chemometric tools enabled botanical and geographical identification of DDGS, as well as the industrial process used to produce them.
A paper based on these results has been published:
Vermeulen, P., Fernández Pierna, J.A., Abbas, O., Dardenne, P. & Baeten, V. (2014). Origin identification of dried distillers grains with solubles using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform mid-infrared spectroscopy after in situ oil extraction. Food Chemistry, accepted.
Contribution
The CRA-W leads the Work Package 1. WP1 will aim to develop a strategy to apply existing methods and new procedures, including fingerprinting methods, and to combine them into a strategy that can be applied to check (on-line, at-line and in the laboratory) the quality of feed materials, to detect non conformity and subsequently to identify adulterants and contaminants. Based on the control report of the several food safety agencies a list of principal contaminants has been established: - Contaminants of industrial origin or introduced through inappropriate drying processes, e.g. dioxins, PCBs, flame retardants - Contaminants of natural origin, e.g. alkaloids, mycotoxins - Contaminants arising from improper use of agrochemicals, e.g. veterinary drugs and pesticides. The work, in a first step, will be mainly performed in three feed matrices: Soybean meals, Vegetable fats & oils and DDGs. In a second step the focus will be in cereals. The CRA-W will also participate to WP2 where the aim is to use existing analytical techniques to prove the traceability and authenticity of feed materials.
Partners
The QSAFFE partners are two universities (QUB, Ireland; CAU, China), seven research institutes (BfR, Germany; CRA W, Belgium; FERA, United Kingdom; JRC-IRMM, Belgium; RIVM, Netherlands; VSCHT, Czech Republic; RIKILT, Netherlands) and two commercial enterprises (Provimi, Netherlands and JOHN THOMPSON & SONS, United Kingdom).
CRAW off coordinator
This project is coordinated by Professor Chris Elliott, Director of the Institute of Agri-Food and Land Use - Queen's University Belfast, UK.Funding
- CE - DG Research - FP7